

195 Cute Cat Names
If you've welcomed a new cat into your home and they need a name, try giving them one of these cute names, including cute names for girl cats, boy cats, orange cats, gray cats, and more.
Luxating Patella in Cats
Luxating patella is an orthopedic condition that affects cats' knees. Learn the causes, treatment, and prevention.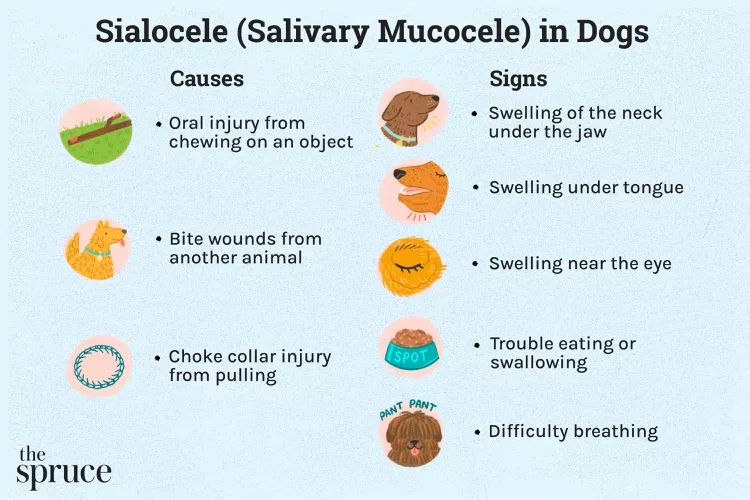
Salivary Mucocele in Dogs
A salivary mucocele, also called a sialocele, causes swelling near a dog's salivary glands and may cause a lump under the chin or on the neck near the jaw. Learn the causes, treatment, and prevention of salivary mucoceles in dogs.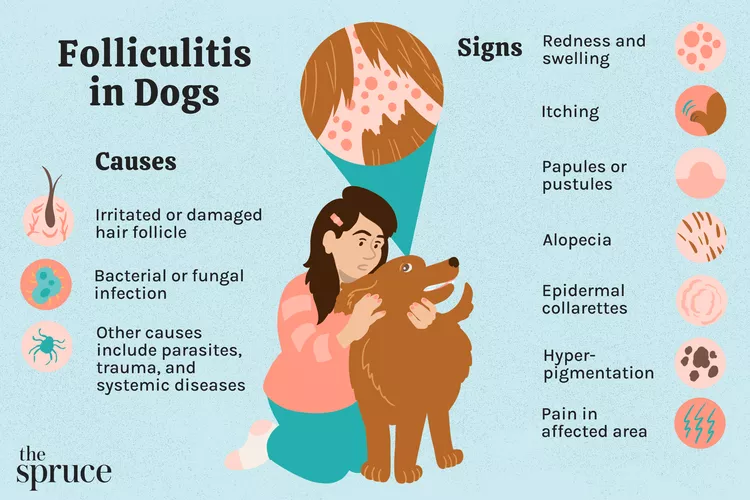
Folliculitis in Dogs
Folliculitis is a common skin condition in dogs. Learn the causes, treatment, and prevention.
Is Baking Soda Bad for Cats?
Baking soda has many common household uses and may help with cat odors, but how much is safe to use around cats?
Can Dogs Eat Parmesan Cheese?
It's no secret that dogs love cheese, but what kinds of cheese should you avoid? Is Parmesan cheese a good option to treat your pup to?
Can Dogs Eat Pistachios?
Dogs can eat pistachios, but only if they're plain and served in moderation. In other cases, pistachios can be harmful for dogs.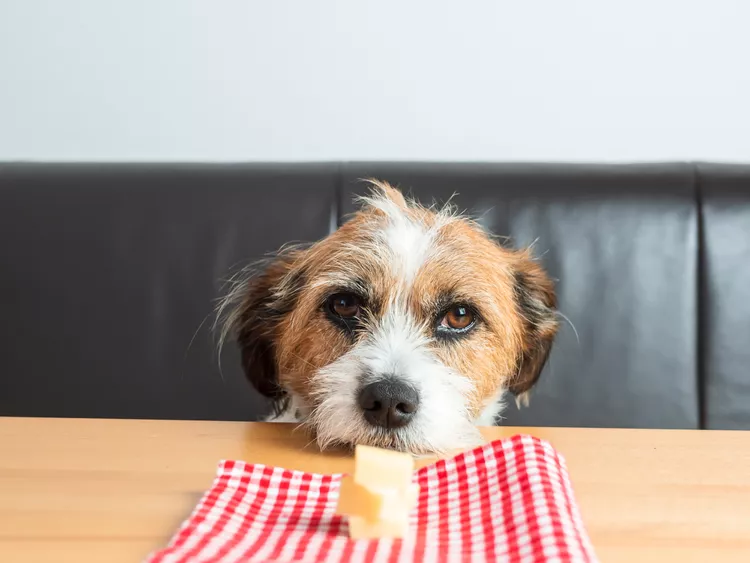
Can Dogs Eat Cheese?
A popular training tool, cheese is OK for most dogs to enjoy on special occasions...but there are some exceptions.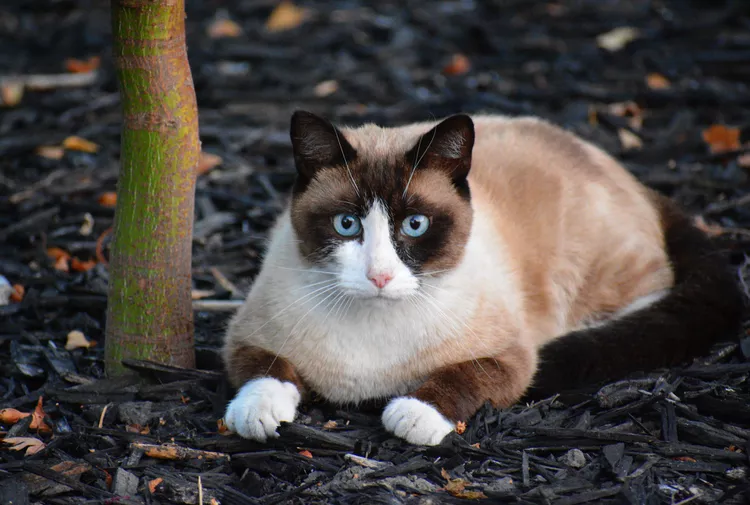
Snowshoe Cat: Breed Profile, Characteristics & Care
The snowshoe cat, a mix of the American shorthair and Siamese, is a smart and affectionate pet that loves company. Learn about the snowshoe cat breed, including temperament, appearance, and care needs.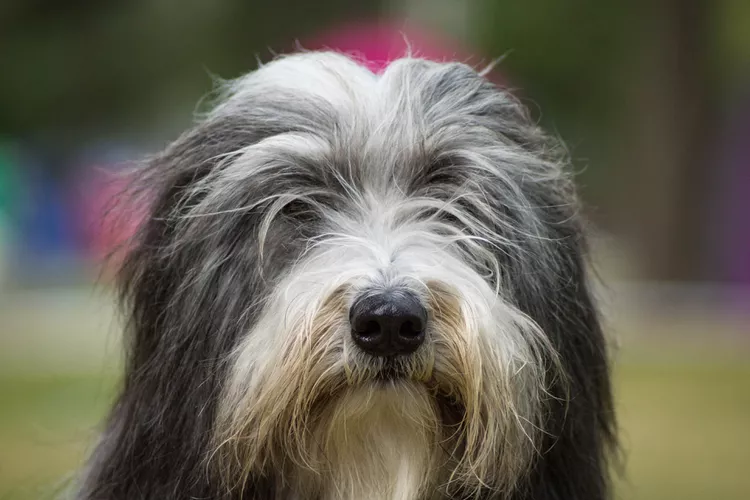
Bearded Collie: Dog Breed Characteristics & Care
Learn about bearded collies, energetic and intelligent dogs known for their herding skills and bearded faces that earned the nickname "beardies."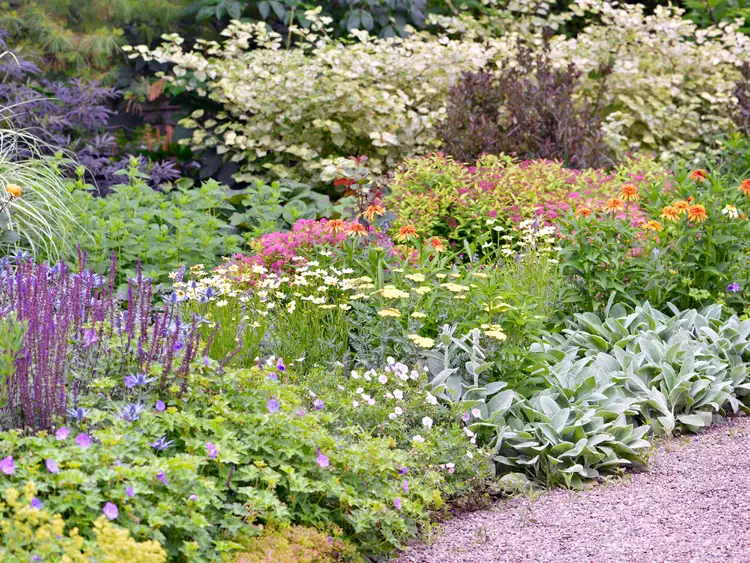
How to Plant a Border Garden that Will Add Color to Your Landscape
Learn how to create a vibrant border garden that will compliment your landscape and provide visual appeal of completeness.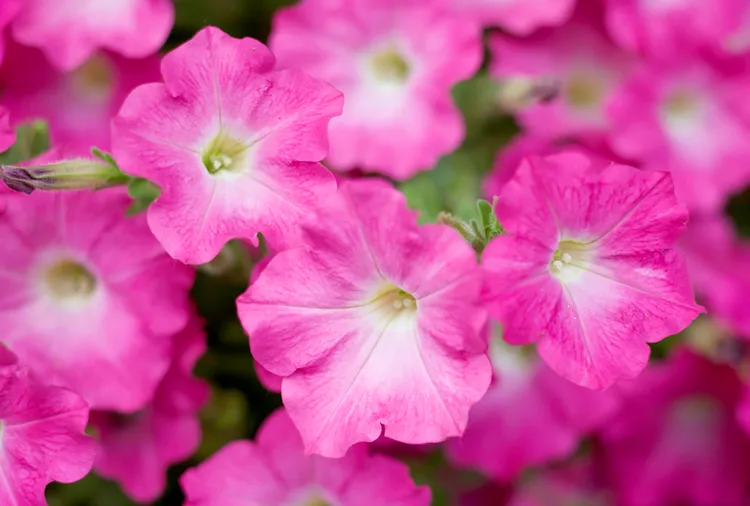
Are Petunias Perennials or Annuals? Plus Tips for Getting Tons of Flowers
Are petunias perennials that come back each year? The answer is yes and no, depending on your climate. Find out how to grow petunias as annuals or perennials.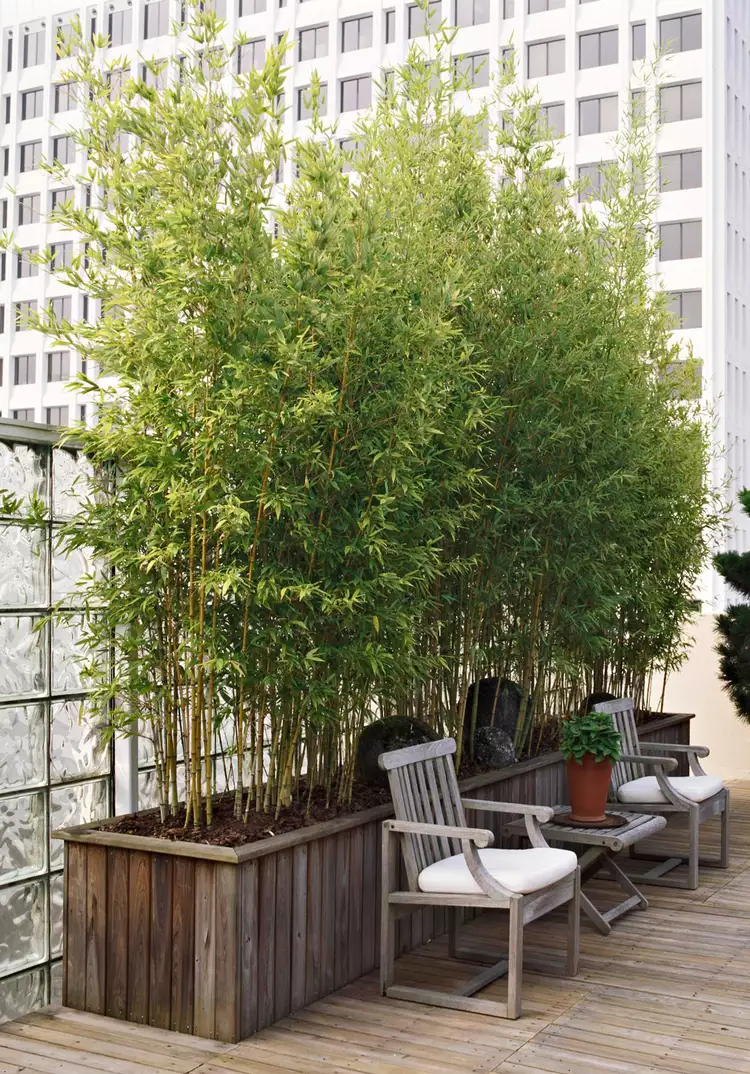
How to Plant and Grow Golden Bamboo
Learn how to grow golden bamboo, a perennial often used for outdoor privacy. Unfortunately, it can be invasive, so be careful where you plant it.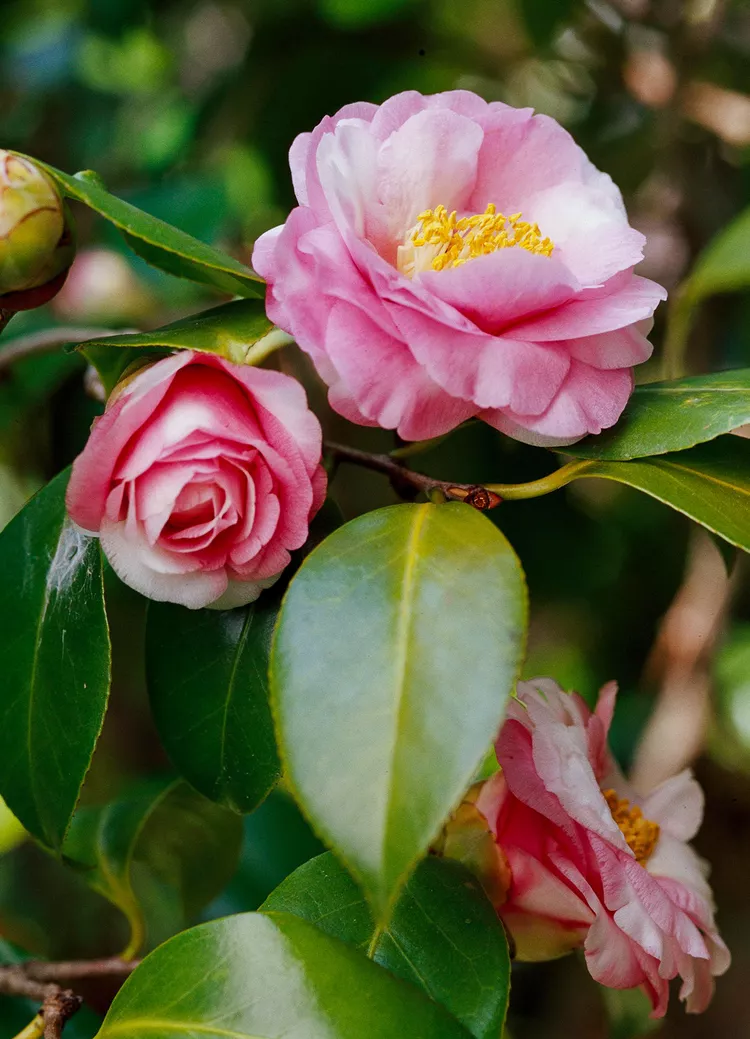
How to Plant and Grow Camellia
Learn to plant and grow camellia, the Southern belles of the plant world. These evergreen shrubs bear beautiful blooms during the colder months.
This Daylily-Filled Garden Plan Lets You Flaunt Your Favorites
Combine daylily varieties of your choice with other reliable plants for tons of carefree color.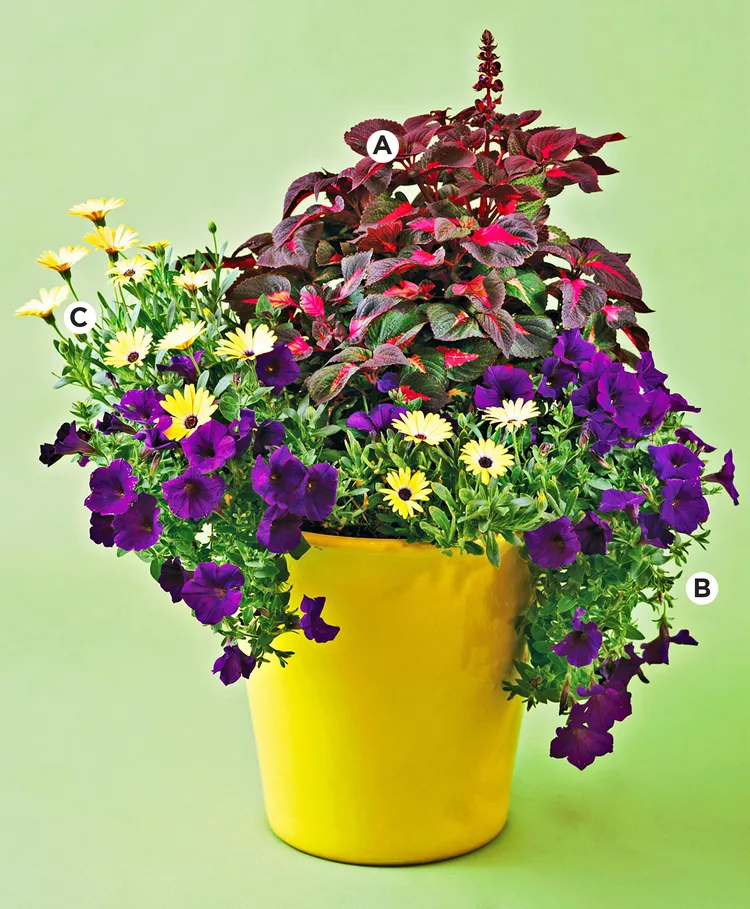
29 Flower Pot Ideas for Stunning Mixes of Blooms and Foliage
Use these flower pot ideas for beautiful combinations to brighten up your porch, patio, or other spots that need a boost of color.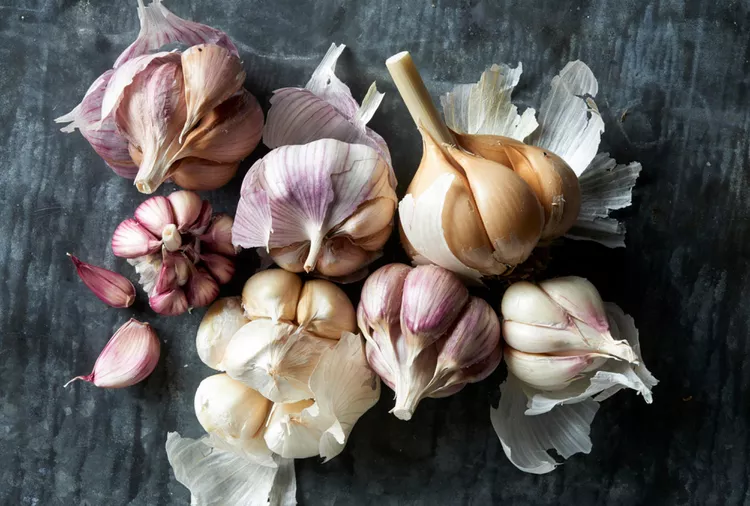
Which Types of Garlic Are Best to Grow in Your Garden?
Hardneck or softneck? Here’s what to know about different types of garlic and how to grow them.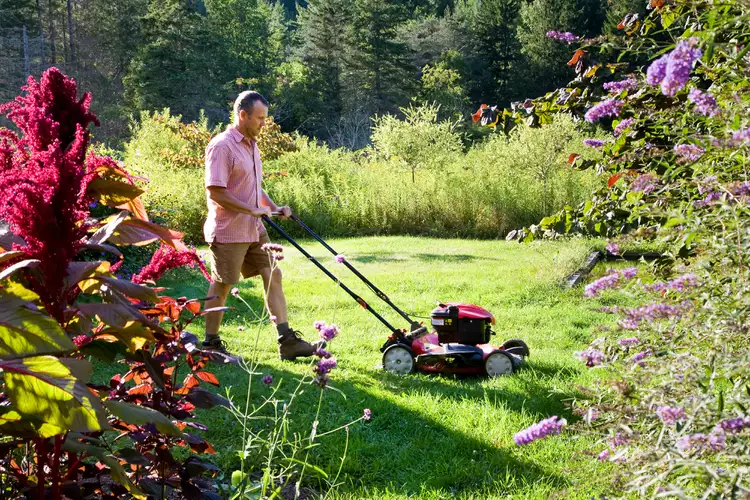
When Is the Best Time to Mow Your Lawn?
Take the guesswork out of deciding when to mow your lawn with our easy-to-follow tips.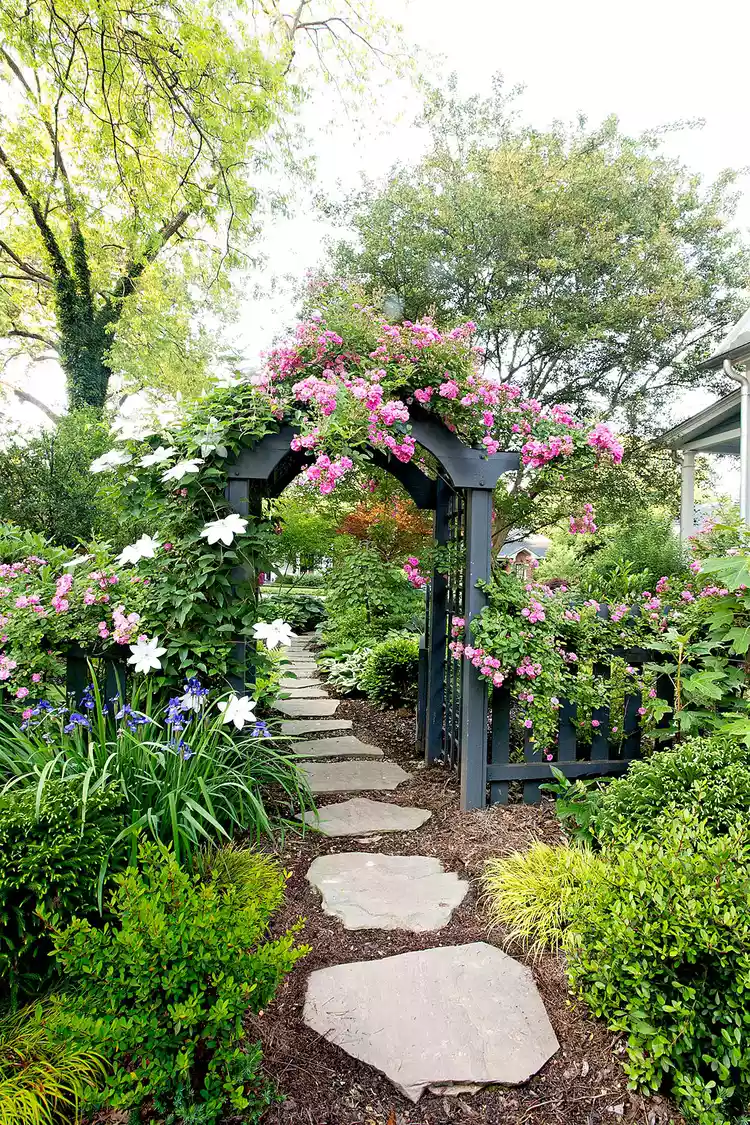
How to Start a Garden: 10 Easy Steps for Beginners
This step-by-step guide explains how to start a garden for beginners. It covers all the basics you need to know, including what to plant, prepping soil, and care tips.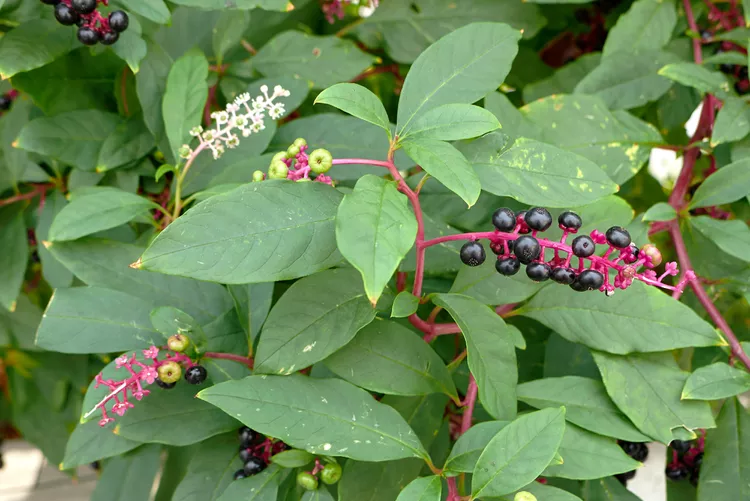
How to Get Rid of Pokeweed in Your Yard
Although this plant is native to parts of North America, pokeweed is still an aggressive, toxic plant you may not want around. Use these tips to safely eliminate pokeweed from your garden.